8 4: Factory overhead variances Business LibreTexts

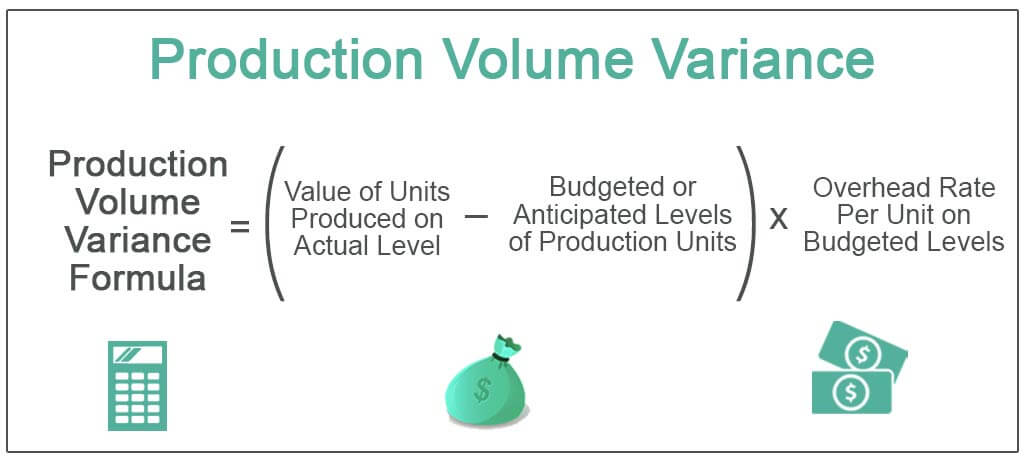
Thus, the variance is created due to variance in the actual production against the budgeted production. The business accounting policy manual is the difference between the amount of fixed overhead actually applied to produced goods based on production volume, and the amount that was budgeted to be applied to produced goods. This variance is reviewed as part of the period-end cost accounting reporting package.
Fixed Overhead Capacity Variance
We will discuss how to report the balances in the variance accounts under the heading What To Do With Variance Amounts. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible.
The fixed production overhead total variance can be subdivided as follows:
Fixed overhead variance refers to the difference between the actual fixed production overheads and the absorbed fixed production overheads over a period of time. The analysis of this variance facilitates a deeper understanding of the fixed costs structure and its behavior in different production scenarios. It allows financial analysts to isolate the impact of production volume changes from other variances such as material or labor, providing a clearer picture of operational performance.
9: Fixed Manufacturing Overhead Variance Analysis
Instead, Jerry’s mustreview the detail of actual and budgeted costs to determine why thefavorable variance occurred. For example, factory rent, supervisorsalaries, or factory insurance may have been lower thananticipated. Further investigation of detailed costs is necessaryto determine the exact cause of the fixed overhead spendingvariance. However, as the name suggested, it is the fixed overhead volume variance that is more about the production volume. Likewise, we can also determine whether the fixed overhead volume variance is favorable or unfavorable by simply comparing the actual production volume to the budgeted production volume.
Likewise, if the actual production exceeds the normal capacity, the result is favorable fixed overhead volume variance and vice versa. Let’s assume that in 2023 DenimWorks manufactures (has actual good output of) 5,300 large aprons and 2,600 small aprons. Let’s also assume that the actual fixed manufacturing overhead costs for the year are $8,700.
- Fixed overhead volume variance occurs when the actual production volume differs from the budgeted production.
- Changes in market demand can lead to fluctuations in production volume, thereby affecting the variance.
- The fixed overhead production volume variance is favorablebecause the company produced and sold more units thananticipated.
- Managers can focus on discovering reasons for these differences to budget and operate more effectively in future periods.
- For example, a consistent negative variance coupled with declining profit margins might suggest that the increased production volume is not translating into proportional profitability, possibly due to pricing issues or rising variable costs.
Specifically, fixed overhead variance is defined as the difference between standard cost and fixed overhead allowed for the actual output achieved and the actual fixed overhead cost incurred. As fixed costs are not absorbed under marginal costing system, fixed overhead volume variance (and its sub-variances) are to be calculated only when absorption costing is applied. Fixed overhead volume variance occurs when the actual production volume differs from the budgeted production. In this way, it measures whether or not the fixed production resources have been efficiently utilized. Fixed overhead volume variance is the difference between fixed overhead applied to production for a given accounting period and the total fixed overheads budgeted for the period.
Consider a company with budgeted fixed production overheads of $10,000 for the coming year. If 11,000 units are produced (pushing beyond normal operational capacity) and each requires one direct labor hour, there would be 11,000 standard hours. If production volume relies on the labor hours of workers and a company implements new efficient practices that reduce the number of hours needed to produce a product, more units will be made than budgeted. The variance can either be caused by a difference in the fixed overheads at a given level of activity or because of a difference in the number of units produced (which affects the absorption of the overheads).
However, output in a standard costing system production will be costed at standard cost. This means that when production enters finished goods we will value it as if it was made at standard cost. This means that as far as fixed overheads go it will be assumed to have been made in 5 hours costing $2 per hour. A portion of these fixed manufacturing overhead costs must be allocated to each apron produced. This is known as absorption costing and it explains why some accountants say that each product must “absorb” a portion of the fixed manufacturing overhead costs.
He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University. Motors PLC is a manufacturing company specializing in the production of automobiles. However if either of these conditions are broken then under or over absorption of overhead can occur.

